Quick Facts About The 8 Planets
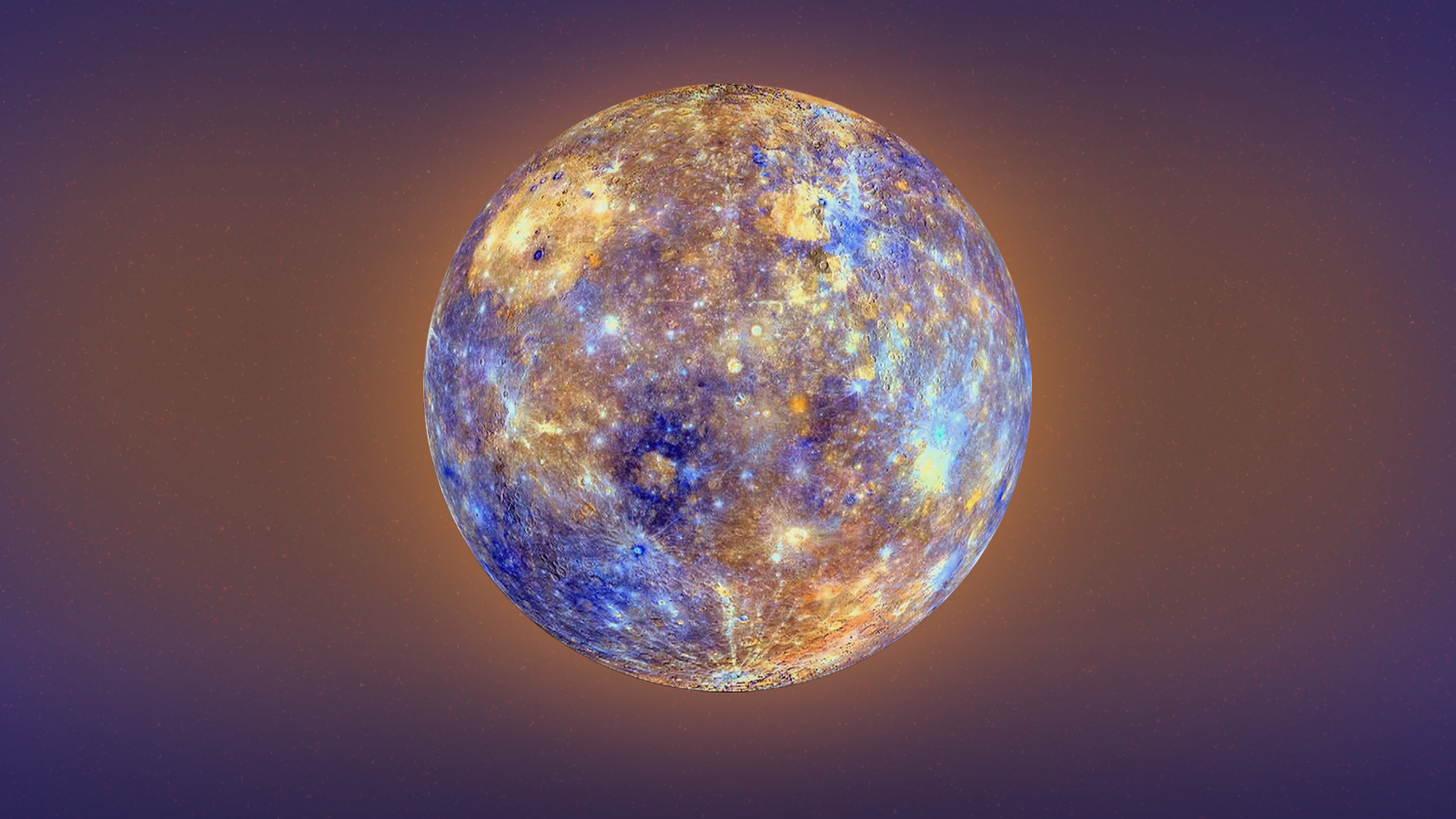
- Distance from the Sun: 57.9 million km - Diameter: 4,879 km - Average Temperature: -173°C to 427°C - Interesting Fact: It is the closest planet to the Sun and has a thin atmosphere. Mercury has a diameter of about 4,879 kilometers (3,032 miles), making it the smallest planet in our solar system. It is approximately 0.38 times the size of Earth. The average distance from the Sun to Mercury is about 58 million kilometers (36 million miles), or 0.39 astronomical units (AU). Mercury is primarily composed of rocky material, with a large iron core that makes up about 70% of its mass. This high metal content gives Mercury a high density, making it the second densest planet after Earth. Mercury's surface is covered in craters, similar to the Moon. It also has extensive plains and scarps, which are cliffs caused by the planet's contraction as its core cooled over time. The largest crater on Mercury is called the Caloris Basin, which is about 1,550 kilometers (960 miles) in diameter. Due to its proximity to the Sun, Mercury experiences extreme temperature variations. During its daytime, temperatures can reach up to 430 degrees Celsius (800 degrees Fahrenheit), while at night, temperatures can drop to -180 degrees Celsius (-290 degrees Fahrenheit). Mercury has a very thin and tenuous atmosphere, known as an exosphere. It consists of atoms and molecules that have been captured from the solar wind and impact from micrometeoroids. The lack of a substantial atmosphere means that Mercury does not have weather or significant air pressure. Mercury has an elliptical orbit around the Sun, with a period of about 88 Earth days. It also has a slow rotation, taking about 59 Earth days to complete one rotation on its axis. This means that a day on Mercury (sunrise to sunrise) is longer than its year (orbit around the Sun). Mercury has a weak magnetic field, about 1% of Earth's magnetic field strength. It is believed to be generated by the planet's molten iron core. Several spacecraft have visited Mercury, including NASA's Mariner 10 in the 1970s and the European Space Agency's (ESA) BepiColombo, which launched in 2018 and is expected to arrive at Mercury in 2025. These missions have provided valuable data and images of Mercury, helping scientists better understand its geology, surface features, and magnetic field.
1: Mercury
2. Venus:
3. Earth:
4. Mars:
5. Jupiter:
6. Saturn:
7. Uranus:
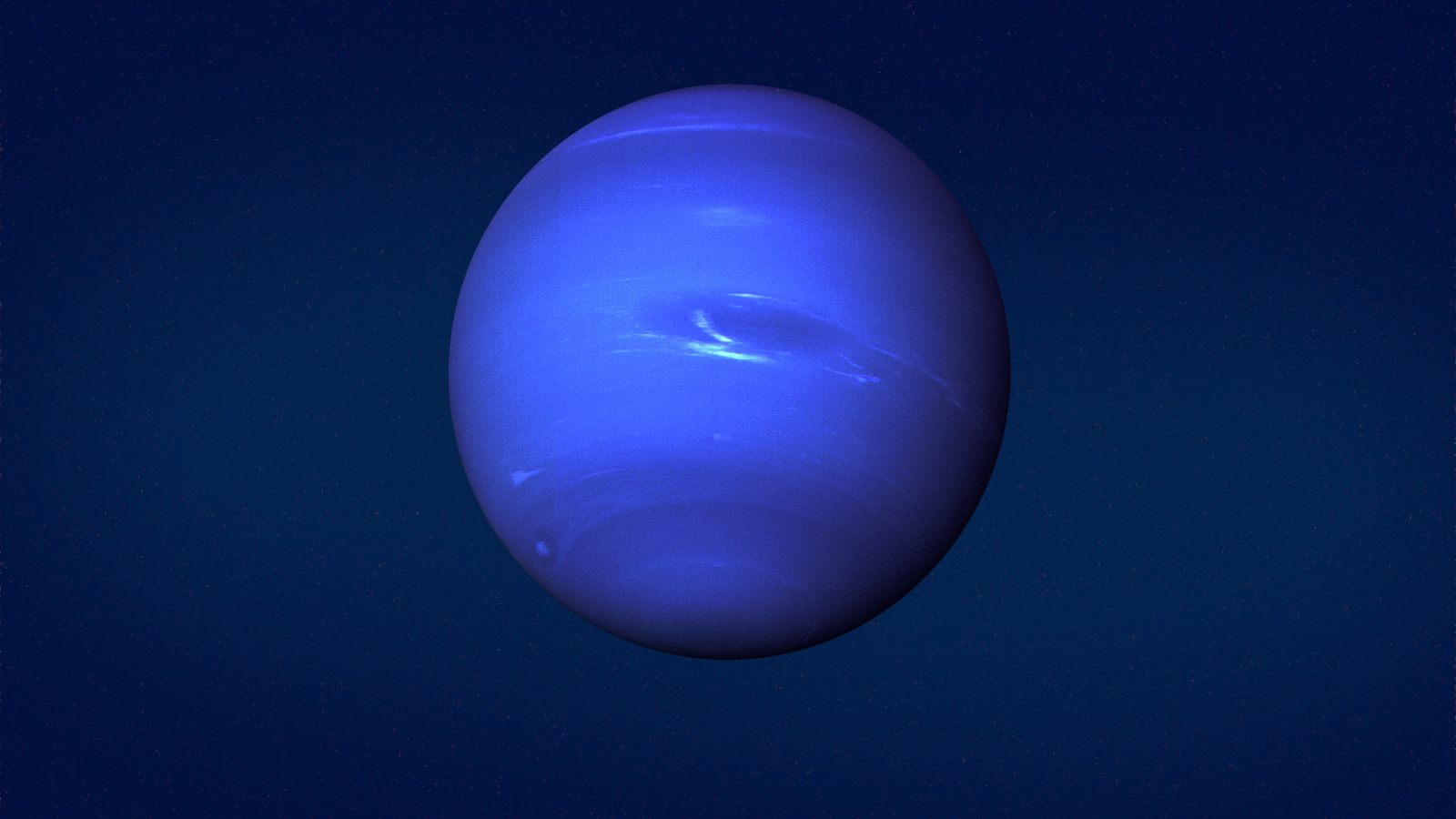
8. Neptune:
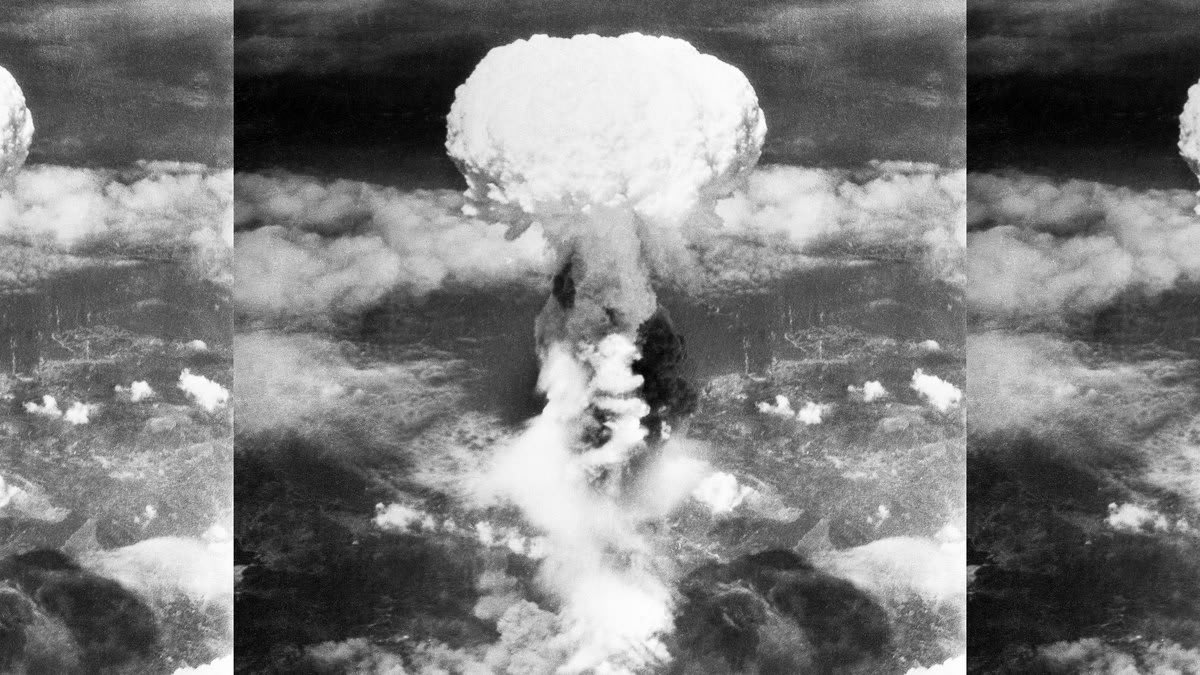
Most Devastating Atomic Bomb
- The bomb exploded approximately 600 meters above the city, releasing an intense burst of heat, radiation, and a powerful shockwave. - The blast instantly killed an estimated 70,000 to 80,000 people and caused severe injuries to tens of thousands more. - The city's infrastructure was lar...
Hiroshima And Nagasaki
1. Hiroshima: - On August 6, 1945, at around 8:15 a.m., the United States dropped an atomic bomb named "Little Boy" on Hiroshima.